Calculation of the roof: how to calculate the angle of inclination of the roof, the length of the rafter and the area of \u200b\u200broofing material
When designing a rafted roof of a private house, you need to be able to correctly calculate the angle of inclination of the roof. How to navigate in various units of measurement, which formulas to carry out the calculation and how the angle of inclination on the wind and snow load is affected, we will talk in this article.
The roof of a private house, erected by an individual project, can be very simple or surprisingly bizarre. The angle of slope of each slope depends on the architectural solution of the entire house, the presence of a attic or attic, used roofing material, the climatic zone in which the loft is located. In the compromise of these parameters, it is necessary to find the optimal solution that combines the strength of the roof with the useful use of the underwear space and the appearance of the house or complex of buildings.

Roof inclination angle units
The angle of inclination is the magnitude between the horizontal part of the design, plates or beams of overlapping, and the surface of the roof or rafters.
In reference books, SNiP, technical literature there are various units of measurement of angles:
- degrees;
- aspect ratio;
- interest.
Another unit of measurement of angles - radians - does not apply in such calculations.
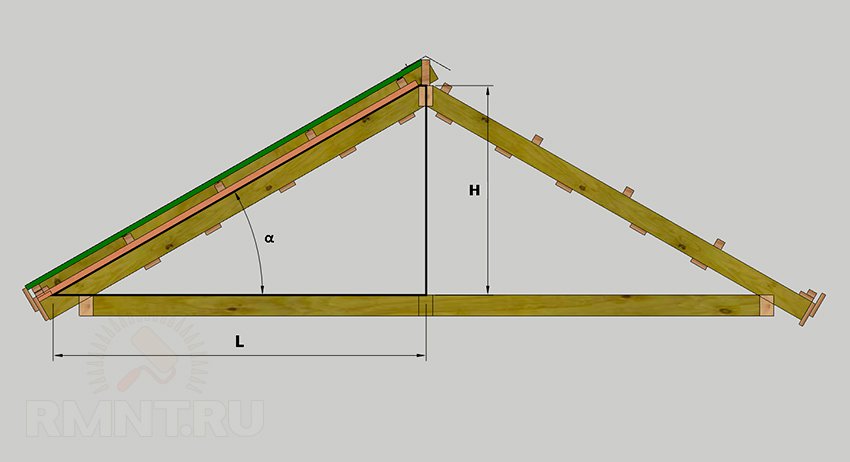
What is degrees, everyone remembers from the school program. The aspect ratio of a rectangular triangle, which is formed by the base - L, height - H (see figure above) and the roof flooring is expressed as H: L. If α \u003d 45 °, the triangle is equilateral, and the aspect ratio (cathets) is 1: 1. In the case when the ratio does not give a clear idea of \u200b\u200bthe slope, talk about the percentage. This is the same relation, but calculated in fractions with percentages. For example, at h \u003d 2.25 m and L \u003d 5.60 m:
- 2.25 m / 5.60 m · 100% \u003d 40%
The digital expression of one units through others is clearly shown in the diagram below:
![]()
Formulas for calculating the angle of inclination of the roof, the length of the rafted and the area of \u200b\u200bthe coating roofing material
To easily calculate the size of the elements of the roof and the rafting system, you need to remember how we solved the tasks with triangles in school using the main trigonometric functions.
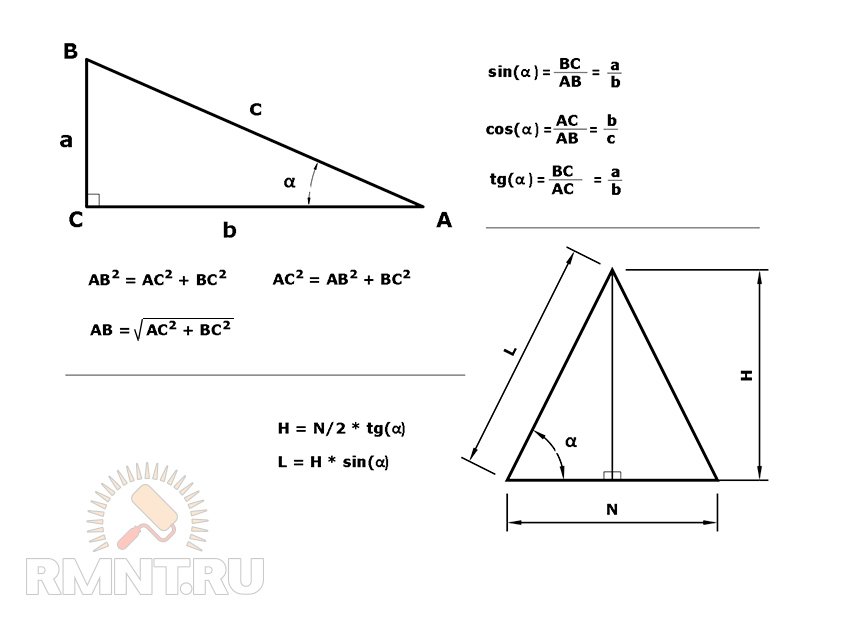
How will it help in calculating the roof? We divide complex elements on simple rectangular triangles and find a solution for each case using trigonometric functions and the Pythagores Theorem.
More complex configurations are more common.
![]()
For example, you need to calculate the length of the rafted the end part of the holm roof, which is an equifiable triangle. From the top of the triangle, we lower the perpendicular to the base and we obtain a rectangular triangle, the hypotenus of which is the middle line of the end of the roof. Knowing the width of the span and the height of the skate, from a broken on the elementary triangles of the structure, you can find the angle of inclination of the hip - α, the angle of inclination of the roof - β and get the length of the triangular and trapezoid sling.
Formulas for calculating (units of measurement lengths must be the same - m, cm or mm - in all calculations to avoid confusion):
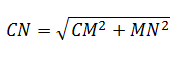
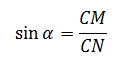
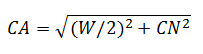
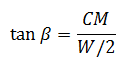
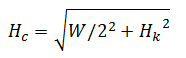
Attention! The calculation of the length of the rafted on these formulas does not take into account the amount of the sink.
Example
The roof is four, hip. The height of the skate (cm) is 2.25 m, the width of the span (W / 2) is 7.0 m, the depth of inclination of the end of the roof (Mn) is 1.5 m.
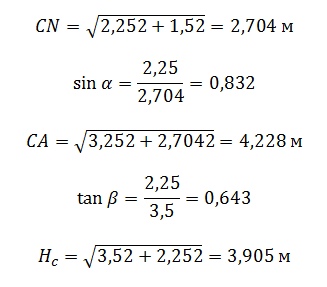
Having obtained SIN values \u200b\u200b(α) and Tg (β), it is possible to determine the value of the corners on the brady's table. A complete and accurate table with an accuracy of a minute is a whole brochure, and for rough calculations, which are permissible in this case, you can use a small table of values.
Table 1
| Roof inclination angle in degrees | tG (A) | sin (a) |
| 5 | 0,09 | 0,09 |
| 10 | 0,18 | 0,17 |
| 15 | 0,27 | 0,26 |
| 20 | 0,36 | 0,34 |
| 25 | 0,47 | 0,42 |
| 30 | 0,58 | 0,50 |
| 35 | 0,70 | 0,57 |
| 40 | 0,84 | 0,64 |
| 45 | 1,00 | 0,71 |
| 50 | 1,19 | 0,77 |
| 55 | 1,43 | 0,82 |
| 60 | 1,73 | 0,87 |
| 65 | 2,14 | 0,91 |
| 70 | 2,75 | 0,94 |
| 75 | 3,73 | 0,96 |
| 80 | 5,67 | 0,98 |
| 85 | 11,43 | 0,99 |
| 90 | ∞ | 1 |
For our example:
- sin (α) \u003d 0.832, α \u003d 56.2 ° (obtained by interpolation of adjacent values \u200b\u200bfor angles in 55 ° and 60 °)
- tG (β) \u003d 0.643, β \u003d 32.6 ° (obtained by interpolation of adjacent values \u200b\u200bfor angles at 30 ° and 35 °)
We will remember these numbers, they will use us when choosing a material.
To calculate the number of roofing material, it will be necessary to determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe coating. Squata area of \u200b\u200ba duct roof - rectangle. His area is the work of the parties. For our example - a holm roof - it comes down to the definition of the area of \u200b\u200bthe triangle and trapezium.
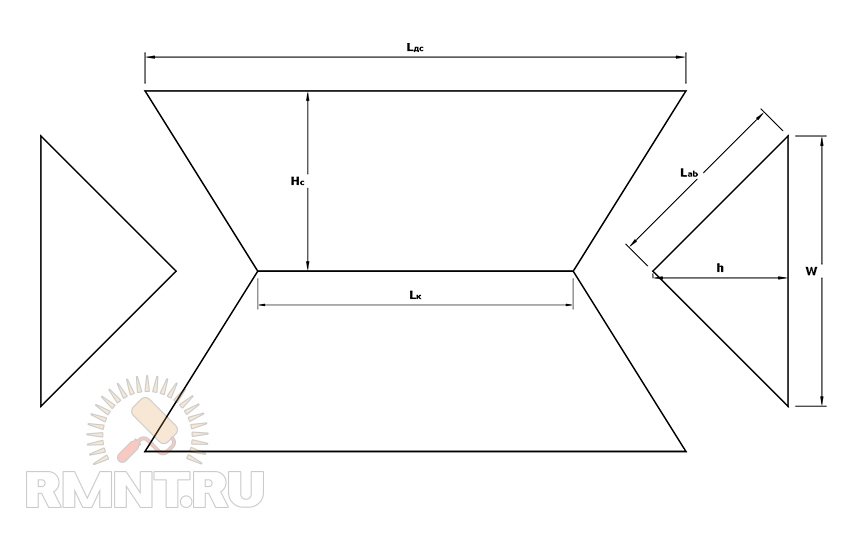
For our example, the area of \u200b\u200bone end triangular slope at Cn \u003d 2.704 m and W / 2 \u003d 7.0 m (the calculation must be carried out taking into account the elongation of the roof beyond the walls of the walls, we accept the length of the sink - 0.5 m):
- S \u003d ((2,704 + 0.5) · (7.5 + 2 x 0.5)) / 2 \u003d 13.62 m 2
The area of \u200b\u200bone side trapezoidal skate at w \u003d 12.0 m, h c \u003d 3.905 m (height of the trapezium) and Mn \u003d 1.5 m:
- L K \u003d W - 2 · Mn \u003d 9 m
Calculate the area taking into account the soles:
- S \u003d (3.905 + 0.5) · ((12.0 + 2 x 0.5) + 9.0) / 2 \u003d 48.56 m 2
Total coating area of \u200b\u200bfour slot:
- S σ \u003d (13,62 + 48.46) · 2 \u003d 124.16 m 2
Recommendations on the inclination of the roof depending on the purpose and material
The non-exploitable roof may have a minimum inclination angle of 2-7 °, which ensures immunity to wind loads. For a normal snow removal, the angle is better to increase to 10 °. Such roofs are common in the construction of household buildings, garages.
If the cerpent space is supposed to be used as a attic or attic, the slope of one- or a double roof should be quite large, otherwise the person will not be able to straighten up, and the useful area will be "eaten by" a rapid system. Therefore, it is advisable to apply in this case a broken roof, for example, an attic type. The minimum ceiling height in such a room should be at least 2.0 m, but preferably for a comfortable stay - 2.5 m.
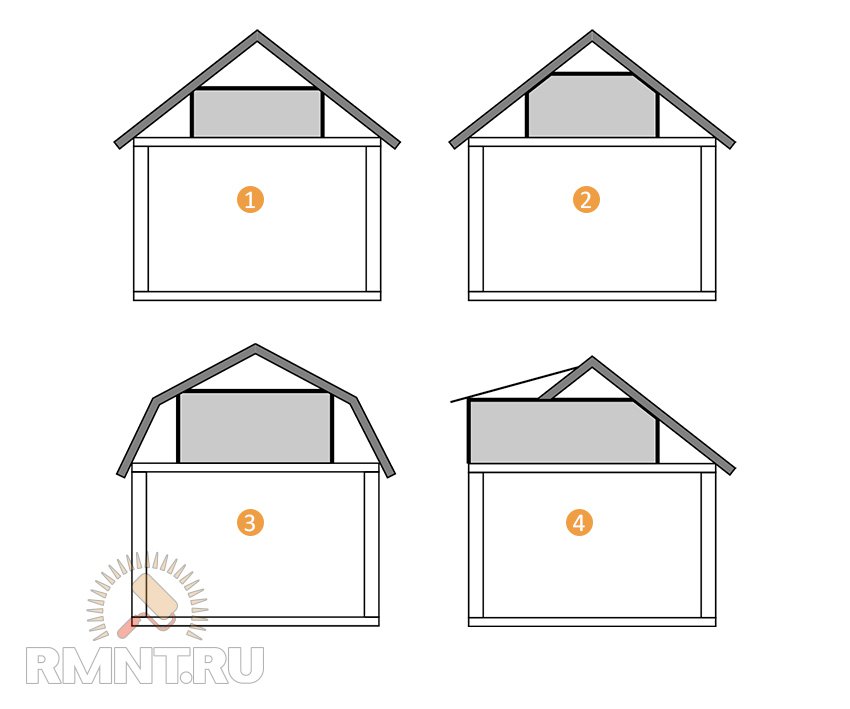 Options for arrangement of the attic: 1-2. Dual-sheet roof is classic. 3. The roof with a variable tilt angle. 4. Roof with remote consoles
Options for arrangement of the attic: 1-2. Dual-sheet roof is classic. 3. The roof with a variable tilt angle. 4. Roof with remote consoles
Taking one or another material as roofing, it is necessary to take into account the requirements for the minimum and maximum bias. Otherwise, problems that require the repair of the roof or the whole house are possible.
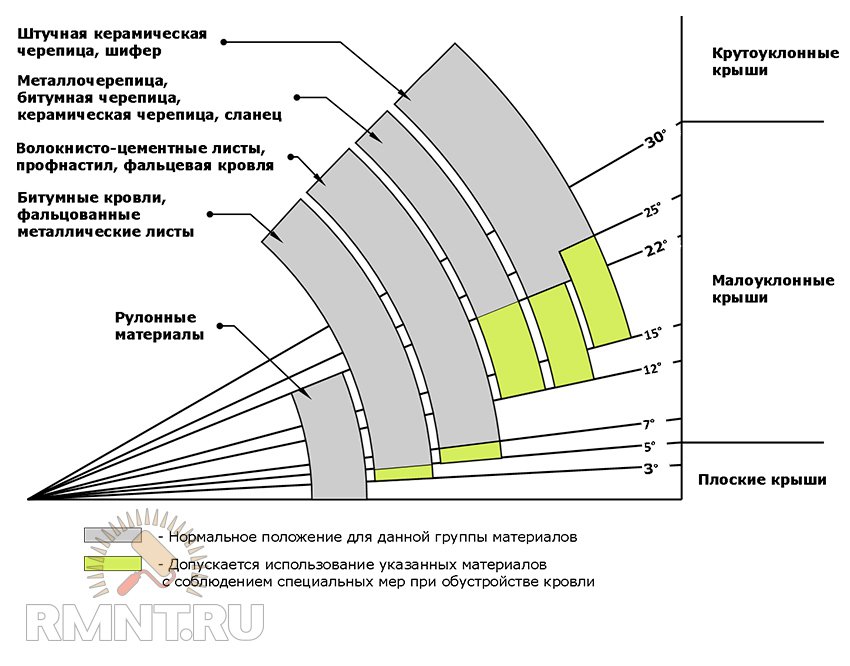
table 2
| Type of roof | Range of permissible installation angles, in degrees | The optimal tilt of the roof, in degrees |
| Roofing from roofing with a spript | 3-30 | 4-10 |
| Thick roofing, two-layer | 4-50 | 6-12 |
| Zinc roofing with double standing folds (from zinc tapes) | 3-90 | 5-30 |
| Fat roof, simple | 8-15 | 10-12 |
| Wall roof covered with roofing steel | 12-18 | 15 |
| Tiling with 4 grooves | 18-50 | 22-45 |
| Rone roofing | 18-21 | 19-20 |
| Tile tile, normal | 20-33 | 22 |
| Professor | 18-35 | 25 |
| Wavy asbestos-cement sheet | 5-90 | 30 |
| Artificial slate | 20-90 | 25-45 |
| Slavic roofing, two-layer | 25-90 | 30-50 |
| Slate roofing, normal | 30-90 | 45 |
| Glass roofing | 30-45 | 33 |
| Tile, two-layer | 35-60 | 45 |
| Golden Dutch Tile | 40-60 | 45 |
The angles of inclination obtained in our example are in the range of 32-56 °, which corresponds to a slate roof, but does not exclude some other materials.
Determination of dynamic loads depending on the angle of inclination
The design of the house must withstand static and dynamic loads from the roof. Static loads are the weight of the rafting system and roofing materials, as well as equipment of the subxurement space. This is a constant value.
Dynamic loads are variable variables dependent on climate and season. To correctly calculate the loads, taking into account their possible compatibility (simultaneity), we recommend to study the joint venture 20.13330.2011 (sections 10, 11 and application g). In full volume, this calculation, taking into account all the possible factors in this article, cannot be set forth.
![]()
Wind load is calculated taking into account the zoning, as well as the features of the location (leeward, atmosphere side) and the angle of inclination of the roof, the height of the building. The basis of the calculation is wind pressure, the average values \u200b\u200bof which depends on the region under construction. The remaining data is needed to determine the coefficients corrective with a relatively constant for the climatic region. The greater the angle of inclination, the more serious wind loads experiencing the roof.
![]()
Table 3.
Snow load, unlike the wind, is associated with an angle of inclination of the roof in the opposite way: the less the angle, the more snow is delayed on the roof, the lower the likelihood of the convergence of the snow cover without the use of additional funds, and the larger loads test.
Table 4.
Come to the issue of defining loads seriously. Calculation of sections, design, and therefore reliability and cost of the rafter system depends on the values \u200b\u200bobtained. If you are not sure about your abilities, it is better to order the calculation of the loads from specialists.






