Technology for planting a lawn on the roof of a house. A flower garden or lawn on the roof - what is it for, and how to create it with your own hands How to make a grass-covered roof
The primary task of the roof structure is protection from cold air, snow, rain or other atmospheric phenomena. However, the lack of space for development, poor ecology in cities, and the low quality of crop products force additional functions to be assigned to the roof, introducing innovative architectural solutions. One of the most current trends in ecological housing construction is considered to be a plant roof, on which you can create not only a lawn, but also a real vegetable garden where you can grow healthy and safe fruits or vegetables. In this article we will discuss whether a green roof can be installed with your own hands.
Roofs on which grass or other plants grow are not a new invention. Although even more ancient examples of this architectural tradition are known, the most significant example of the use of vegetable roofs is the turf dwellings of the Icelanders, which date back to the 18th century. Moss-covered houses are a characteristic feature of the peoples living in the territory of modern Norway, Canada, Great Britain, and Switzerland.
Residents of the country, which is characterized by a harsh, cold, windy climate, immediately noticed that a roof covered with vegetation better protects against low temperatures, retains heat inside the house, creating a pleasant microclimate for living inside the home. In modern conditions, eco-roofs, used for planting a lawn or setting up a mini-vegetable garden, are rather a fashionable trend that allows you to take care of nature, your own health and rationally organize your living space.
It is interesting that in modern megacities, where the level of air pollution and stress exceeds all reasonable limits, it is necessary to organize green recreational areas for people. Even in the projects of Soviet modernist architects, eco-roofs appeared, designed for walking, relaxing, or placing greenhouses that could provide residents with fresh greenery all year round.

Advantages
Widespread landscaping is a necessary condition for a comfortable life in modern cities built of glass and concrete. However, often in cities covered with asphalt there is simply not enough space to accommodate green areas. The way out of this situation is a green roof, which allows not only to use living space more efficiently, but also to significantly improve the environmental situation. The advantages of this technology include:
- Durability. The plant layer that tightly covers the roof surface protects the roofing material from mechanical damage, temperature changes, and moisture, so it will last more than 20 years.
- Rationalization of the use of rainwater. Green spaces located on the roof slopes retain more than 25% of precipitation, preventing spontaneous water runoff and flooding. Instead of being wasted into storm drains, the water is used for irrigation and feeds crops.
- High insulating properties. The layer of soil and turf on an eco-roof serves as an excellent insulating material, which helps maintain a comfortable temperature inside the home and protects from external noise.
- Organization of additional living space. A green roof can become a place for relaxation, outdoor sports, swimming pools and even a cafe.
But the most important thing is that the technology of arranging eco-roofs makes it possible to improve the environmental situation in completely polluted megacities, preserve and increase the health of modern people.
Flaws
Despite the obvious advantages, the technology for installing green eco-roofs has not yet become widespread. This is primarily due to the high complexity of installation and the large number of costs for installation and maintenance of the structure. The disadvantages of plant roofs are considered to be:
- Heavy weight. A layer of drainage, soil and plants adds up to 50 kg/m2 of area, so the green structure significantly increases the load on the floors and foundation of the structure.
- High price. To install an eco-roof, it is necessary to use only environmentally friendly materials, so its installation is much more expensive than a conventional pitched or flat roof.
- Difficult to install. Due to the heavy load on the foundation and floors, installation of a plant roof requires a project based on accurate calculations. Therefore, it is quite difficult to do this work with your own hands; most often you have to resort to the services of contractors.
Note! Most experienced roofing craftsmen and architects believe that it is dangerous to convert an old roof into a plant roof, since the floors and foundation may simply not withstand the additional load and cause irreversible deformations.
Kinds
Depending on the height and purpose of the building, the types of plants used and the landscaping goals pursued, an eco-roof can change its appearance. It can be successfully installed on both pitched and flat roof structures. Depending on the nature of use, the following types of vegetable roofs are distinguished:

Important! In order for a green roof to please with its aesthetic appearance for a long time, it is necessary to carefully select plants that tolerate climatic conditions in the region where construction is taking place and are not demanding in care. In addition, it is worth considering that the thickness of the soil layer is limited, so you should choose plants whose roots are located not vertically, but horizontally.
Structure
Eco-roofs, just like conventional roofs, resemble a layer cake in their structure, however, their components are slightly different due to the characteristics of their operation. They must ensure structural reliability in the following areas: foundation strength, protection against water penetration, and prevention of heat loss. The roofing pie of vegetable roofs has the following structure:
- Base. The base of the roof can be wood or concrete, the main thing is that it has a sufficient margin of strength to withstand the weight of the soil and plants.
- Waterproofing. To protect against moisture penetration, waterproofing material is laid on the base in several overlapping layers. Moreover, it must have increased strength.
- Barrier. A root barrier is placed on top of the waterproofing, which should prevent plants from growing below this level. Without this layer, roots will grow into the waterproofing material, damaging it.
- Drainage. A drainage layer is necessary to rationally distribute moisture entering the soil. It retains some of the water, preventing plants from drying out during dry periods, and directs the excess into the drain.
- Filter. A filtration layer or geotextile is spread over the drainage to limit the penetration of small particles that can clog it.
- Geogrid. The geogrid prevents the soil from sliding down and scattering when exposed to wind. It is most often used if the slope is more than 25 degrees.
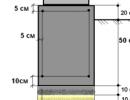
- Substrate. The fertile substrate is poured in a uniform layer 5-20 cm thick onto the geogrid. To grow a lawn, a soil layer of 5 cm is enough, but to grow fresh cucumbers on the roof you will need a depth of 20-25 cm.
Please note that the soil for an eco-roof should be quite light, but retain moisture well. Landscape designers recommend using fine expanded clay, peat and sand for lightening. In addition, it is worth taking care of soil fertility by adding organic and mineral fertilizers.

Selection of plants
To prevent the plant roof from withering away in the first dry summer or from freezing in the cold winter, it is necessary to select unpretentious and winter-hardy plants that can exist well in a closed ecosystem. Landscape designers and plant growers recommend adhering to the following rules when selecting flora:
- Small and horizontally located root system. Mosses and grasses best meet this criterion.
- Frost resistance. Plants must be able to withstand freezing temperatures typical of winter.
- Drought resistance. It is necessary to choose plants so that they only need natural watering during rain.
Remember that exotic plants that are not typical for our climate zone require more careful care, so you can plant them only if you are prepared to spend a lot of time and money to provide them with appropriate living conditions.


Video instruction















Among the wide variety of roofing coverings, there is one type called green roofing. Essentially, it is grass that is planted on the roof of a house. Therefore, that article will talk about how to plant a lawn on the roof of your own house. What are the advantages of this roofing covering, and are there any disadvantages? What technologies are offered today to make the grass on the roof grow lush, giving the building an unusual appearance?

A little history
The grass roof is not new. We can say that this is one of the oldest ways to protect a house from weather conditions. This coating was used in ancient times in Russia and in northern European countries. Moss was used in Scandinavia. In Russia, a thatched roof was additionally covered with turf, thereby protecting one’s home from fires.
Gradually, these roofs began to be forgotten. But the famous architect Karl Rabitz, who invented the grouse grid, which is named after him, has again revived the concept of a “green roof”. In the 19th century, at the Exposition Universelle in Paris, he provided a model of a grass-covered house. The surprise of the visitors knew no bounds. Many people liked the idea, which gave rise to the revival of forgotten technologies.

Types of roof lawn
The easiest way to create a grass roof is to use container gardening technology. This is when grass is planted in special boxes or boxes that cover the roof area of the house. This landscaping option is convenient because there is no need to prepare the surface of the roof itself for planting plants. The latter grow in containers. If necessary, they can be replaced with a new box or rearranged.
The technology of laying turf is a solid base on which soil is poured. And only then grass seeds are planted in it. Or plant turf in rolls on prepared soil. There are two main technologies here – the intensive method and the extensive one.
The first is difficult in preparing the soil layer, the thickness of which varies between 1-1.5 m. It must be carefully looked after. But you can safely walk on such a green roof, build platforms and paths, and even build gazebos. In addition to grass, shrubs and dwarf trees are planted in the ground, which is why the thickness of the soil layer is so large.
The second one is unpretentious and does not require special care. But it does not tolerate stress well, even from the weight of a child. Therefore, this variety is mainly used to cover steep roofs - with a slope angle of no more than 45 0. The thickness of the soil layer here is small - 15 cm.

On our website you can get acquainted with the most . In the filters you can set the desired direction, the presence of gas, water, electricity and other communications.
Lawn on a flat roof - how to make it
The simplest solution is to install a grass roof on a flat roof. If you work hard, you can subsequently organize an excellent recreation area. We will assume that the roof of the house is covered with a built-up roof. For flat roofing structures this is the ideal option today, durable and inexpensive.
To create a lawn required:
geotextiles;
special membrane with convex large bosses on the front surface;
double sided tape for fastening geotextiles and special adhesive tape for the membrane;
peat substrate;
rolls of finished lawn.

All this is sold in stores, which means you won’t have any problems purchasing it. There may be problems with the price, but if you have finally decided to install a lawn on the roof of your house, then you should not avoid the expense, especially in terms of saving. That is, it is recommended to use these materials. Although expanded clay instead of a membrane is also suitable.
So, why is geotextile needed? Its task is not to allow plant roots to pass through, which can damage the layers of the fused roofing and under-roofing carpet. That is, they can disrupt the integrity of the roof covering, thereby causing roof leaks.
Why is a membrane needed? This is a layer of polymer material that organizes drainage. The space between the bosses is the drainage system, through which excess moisture and precipitation will be removed.

Sequentially laying layers of green roof
You need to start by cleaning the roof plane. They simply sweep it with a broom, removing dust and debris. Further in this sequences:
Lay out geotextiles stripes overlapping relative to each other with offset edges within 10 cm. The edges of the material are glued together with double-sided tape.
Lay out the membrane in the same direction as geotextiles. Laying is done with an overlap and gluing with a special tape. Both layers (membrane and geotextile) are also glued together with adhesive tape.
Another one is placed on top of the stacked materials. geotextile layer, only in the transverse direction.
The basis for the landscaping structure is ready, cover the peat substrate. It is evenly distributed over the entire area of the flat roof. The optimal backfill thickness is 4-5 cm.
Now spread rolls of grass. Some people recommend doing the layout in a checkerboard pattern. But, as practice has shown, this is not the most important point in the construction of a grass roof.
All that remains is water the lawn well. After a few days, the seams between the laid rolls will not be visible.
Video description
The video shows how to make a green lawn on the roof of your own house:
This is a classic way to plant grass on the roof of a house (the technology is not only simple, but also inexpensive). Another option is to plant vegetation seeds in prepared soil. In fact, all the above-mentioned layers are laid in the same order. Only the peat substrate is mixed with the soil, and then this mixture is scattered onto geotextiles. After leveling, seeds are planted in it and watered abundantly.
In principle, this option is not so difficult, but here you have to wait for the grass to grow. At the same time, there is always a possibility that in some areas there will be less or more of it. And not all sprouts will be accepted. Therefore, it is optimal to purchase ready-made herbal rolls. They are already adapted to growth; the main thing is to maintain the required water balance and temperature conditions. Although the rolls are also adapted to the temperature.

Advantages and disadvantages of a green roof
Let's start with advantages:
This is first and foremost unusual. Thus, you can stand out among your neighbors in the holiday village.
More green– more oxygen.
Grass cover – additional layer, restraining heat loss through the roof structure. And this means saving thermal energy and money allocated for heating the house.
Sound insulation improves.
Opportunity organize an excellent recreation area, but you will have to take into account the degree of load-bearing capacity of the roof itself.
Concerning shortcomings:
You'll have to spend all your time behind the grass roof care.
She increases wall loads and the foundation of the building.
A stronger structure will have to be built under it. roof structure taking into account a more complex waterproofing system.
These are additional financial investments.

Conclusion on the topic
Lawns on the roof are technologies that have long been worked out to the smallest detail. Many people today are trying to do something unusual in their suburban area. Many companies offer this service. It's not that cheap. By choosing a green roof, you additionally get not only a beautiful landscape design, but also an original approach to the design of your yard.
The history of roof gardens began with Assyria, Babylon (the famous terraced gardens of Babylon), then gradually similarities of these gardens began to appear in Greece, ancient Rome, from the beginning of the 17th century in Northern Europe (Germany, Sweden) and in Russia (famous hanging gardens Kremlin).
Over time, as the industry of building materials and structures developed and improved, roof gardens began to appear all over the world - in the USA, Canada, Japan and many other countries. Grass roofs, flat and pitched, also have their own ancient history - they are mainly characteristic of buildings in Norway, Sweden, and the Baltic countries - where they are still being built.
For green roofs, in addition to the traditional design, builders recommend using inversion roofing
(remember that in its design the insulation is located on top of the waterproofing). It is this coating laying technology that best ensures the durability and reliability of waterproofing, preventing uneven deformation of layers due to dynamic loads and temperature differences.
An inversion solution may be appropriate, for example, when landscaping an old flat roof, on which it is undesirable to deform the existing waterproofing coating. To do this, the roofing waterproofing is restored or covered with a new waterproofing layer. After this, rigid insulation is laid. It is only important to make sure that the house structure can withstand the additional load.
Traditional Norwegian turf roofs
The roofs of buildings can be covered with turf and grass. Roof gardens are not just a roof covered with turf and planted with trees and shrubs, but a unique, well-thought-out and competently implemented garden landscape design, beauty!
Despite the fact that roof gardens are quite common all over the world, for Russians they are still something new and something surprising.
Vegetable layer of the garden:
reduces harmful electromagnetic radiation
protects the roof from ultraviolet rays
serves as additional roof insulation
protects it from mechanical damage
The selection of plants for greening roofs must meet a number of criteria. On the roofs of high-rise buildings, plants find themselves in different microclimatic conditions, as if close to mountain ones - high solar radiation, wind, sharp temperature fluctuations, hard artificial foundation. Under these conditions, plants have a much lower ability to withstand climate change than on land. A positive factor is a decrease in the concentration of harmful substances for plants in the air at a significant height from the ground.
There are two types of roof greening: extensive and intensive. The only limitation on green roofing is the stability of the roof structure. The requirements for extensive landscaping are softer than for intensive landscaping. Unfortunately, green roofs are rarely used in Russia, but recently the demand has been growing.
________________________
Roof Garden Plants:
Quince is low
Aronia chokeberry
Barberry Thunberg
Birch is low
Hawthorn prickly
Amur grapes
Maiden grapes
Derain white
Canadian spruce
Prickly spruce
Norway spruce
Alpine honeysuckle
Honeysuckle blue
Goat willow
Viburnum common
Cedar dwarf
Cotoneaster brilliant Maple Ginnala
Tatarian maple
Silver goof
Juniper horizontal
Juniper Cossack
Juniper prostrate
Mountain ash
Golden currant
Snowberry white
Mountain pine
Spiraea sharp-toothed
Spiraea japonica
Thuja occidentalis
Mock orange crown
Niedzvetsky apple tree
Siberian apple tree
and etc.
And also - sedums, sedums, thyme, young grass, bluegrass, fescue, plantain, sedum, saxifrage, carnation grass and many others.
The main thing in green roofs is the arrangement of soil layers in which plants can feel just like in their natural habitat. The main layers are: a moisture-protective layer, a membrane to protect against the penetration of plant roots, a filter fabric (allows water to penetrate without washing away the soil), a moisture-retaining coating (necessary to maintain sufficient moisture in the soil), a drainage system to remove excess water, soil, seeds and the plants themselves. The soil should be easily saturated with water, while retaining sufficient moisture for plant life and growth. Broken bricks and other recycled materials are often added to the soil.
Option 1 (Norwegian technology)- the so-called “double-shell roof”, in which a ventilated cavity is provided between the lower insulated layer and the grass covering. The advantage of this design is that water vapor generated in residential premises “diffuses” through the vapor-permeable thermal insulation and then escapes into the atmosphere. The grass covering in such a roof is laid in two layers - one layer with the grass facing down - for better heat accumulation. However, if the slope of the roof slopes exceeds 22 degrees, the turf will slide, and special mats made of “clawed” fabric will have to be laid between the layers.
Option 2 (German) is distinguished by the peculiarity of laying thermal insulation - on top of the root protective shell, and not in the cavity between the rafters (Norwegian version). This reduces the cost of the entire structure, since an additional intermediate layer of fabric is not needed. However, if the insulation board is chemically incompatible with the root protection film, the roof will quickly collapse.
Option 3 – “flat roof” technology- one of the most popular in Russia and often used in urban construction - is good because it does not require special devices to prevent soil sliding. But at the same time, the base of such a roof must be absolutely sealed, otherwise the roof may leak.
Green roofs are a relatively new trend in modern construction, but they are increasingly being used in Europe. Approximately 10% of houses in Germany are built using Green Roof technology, and the industry providing such materials and services is growing by 10-15% annually.
Because of its advantages, European countries and Germany in particular include the construction of Living Roofs in their building standards and issue subsidies to encourage “Green Building”.
In Russia, thatched roofs were covered with turf to prevent fire, and then vegetation grew on this turf.
There are two types of roof greening: extensive and intensive. The only limitation on green roofing is the stability of the roof structure.
Extensive method gardening is the simplest. It is often used on the roofs of industrial enterprises in developed European countries. And outside the city, this method is used to green the roofs of garages, gazebos, terraces and various outbuildings. At the same time, people are not expected to have access to such a roof. The main component is ground cover plants - sedums, saxifrage, some bulbous or just lawn grasses. The maximum permissible roof slope in this case is 28o.
The roof surface is protected from plant roots with a special film that prevents horses from destroying the roof. And to reduce the pressure of the vegetation layer on it, a geotextile or geotextile is used. The parameters of the canvas, such as density, thickness, structure, depend on the design of the building, that is, the expected load. Roofs with a slope of less than 4o must be equipped with a drainage system, otherwise water will stagnate in the soil, and as a result, the load on the roof will increase.

As a basis for planting plants, a fertile layer or substrate with a thickness of 5 to 20 cm is poured, similar to ordinary lawns. With a limited thickness, up to 10 cm, the layer must be sufficiently mineralized. To prevent the substrate from mixing with the drainage over time, the layers of drainage and substrate are also separated by a thin geotextile. Since such a lawn on the roof exists on its own, landscape designers select plants that require minimal care. Gradually, a kind of lawn forms on the roof, other plants and even birds take up residence.

Extensive gardening technology:
1. Roofing material
2. Protective film (water-repellent membrane)
3. Drainage layer
4. Geotextiles
5. Soil substrate
6. Plants 

School of Art, Design and Media at Nanyang Technological University. A grass roof not only looks cool, but also performs some important functions: it cools the air, collects rainwater, which is then used for irrigation, and most importantly, allows students to get together after classes (or instead of them), lie on the grass and carry out their usual activities, in general. , student lifestyle.
Intensive landscaping imposes serious restrictions on the building design (it must withstand from 150 kg to 750 kg per square meter). Intensive greening of the roof will allow you not only to contemplate the green lawn on the roof of the house, but also to relax on it. If the strength of the structure allows, you can arrange a real garden on the roof with ponds, fountains and lush flower beds, lay out paths, and put up benches. You can plant trees up to 4 meters high - coniferous, deciduous. Naturally, large plants and trees require a larger fertile layer; on the roof it can be more than one meter. With such a thickness, fairly large trees are planted. The drainage layer will be at least 20 cm. In order not to run across the roof with a watering can or hose, watering planted trees, you need to provide an automatic watering system in advance.
_______________________
To build a modern, reliable turf roof on a roofing felt, a layer of “Plato’s rugs” is not enough. These thick plastic mats provide an extra layer of waterproofing, with knots on the top side providing good grip on the turf and good ventilation on the bottom.
The rugs are laid with the knots down so that there is good ventilation between them and the roofing felt.
For a durable roof, it is better to lay two layers of turf. The first is placed on the mats with the roots facing up, the second with the grass facing up. If the roof slope is more than 15 degrees, then a thin mesh is laid between the layers of turf - from one overhang to another, thrown over the ridge.
If only one layer of turf is laid, then it is placed with the roots facing up, after which the turf is sown.
The turf roof is heavy. One square meter of I turf weighs approximately 150 kg, one square meter of double layer - 250 kg. Before installing such a roof, ask a specialist to calculate whether its structure can withstand such a load.

Roof gardens in San Marino

A private option for intensive landscaping.
1.
2.
3.
One of the most famous examples of green roofs is the Gardens of Babylon - one of the Seven Wonders of the World. Turf roofs have graced homes in Scandinavia and Central Asia for thousands of years. In Europe, the first roof garden was installed by the Swedish architect F. Hundertswasser.
The fashion for green roofs in Europe has existed for about thirty years. The thatched roof is also popular there, which looks original and attractive. Today, the turf roof is one of the most promising areas of urban construction. In Russia, this innovation is just beginning to enter the roofers’ toolkit. Turf roofs have become most popular in big cities. The fact is that land there is expensive and it is simply impossible to create gardens on the ground. Such roofs abroad are not only welcomed, but also encouraged financially.
Turf Roof - Benefits
In addition to giving an incredible appearance, green roofs provide tangible results in reducing air pollution. Such a roof also protects from the summer heat, which is especially pleasing to owners of apartments on the upper floors. Unlike bituminous materials, which, when exposed to temperature, begin to emit various fumes, a green roof is absolutely clean. In addition, by reducing the heating of surfaces, it is possible to reduce the air temperature in the city, as well as clean it. Turf roofing is one of the sources of oxygen in the city.

In addition to this, a green roof allows rainfall to be regulated. The coating retains a significant portion of storm water and also purifies it of heavy metals and other harmful substances. It is quite possible to organize a small vegetable garden on green roofs. This opportunity quite realistically allows us to solve some food problems. In addition, various birds are happy to settle on these, and with their singing and presence they can bring joy to the residents of the house.
Types of green roofing
Completely different types of roofs can be greened - flat, single-pitched, gable and others. The basic rule to follow is that the slope should not exceed 40 degrees. Depending on the slope of the slopes, the appropriate landscaping system is selected.

For pitched roofs with an angle of up to 40 degrees, it is necessary to additionally use special gratings that are designed to prevent vegetation from sliding down.
According to its type, turf roofing is divided into three types. They differ in functionality, method of landscaping, load on the foundation and walls.
The intensive type of gardening allows you to create real gardens that include various ornamental plants. Landscaping can be done in several levels. Such roofs allow you to install alpine slides and small ponds. That is, this type of roof is suitable for full-fledged landscape design. Such a roof requires appropriate care and watering, so it is necessary to properly organize the plant irrigation system. It is imperative to develop a design for such a roof, according to which installation work will be carried out.

Extensive landscaping differs from the previous type of roofing in that you cannot walk on it. Planted plants grow as if in wild conditions, with minimal human intervention. Such roofs exclude the possibility of human movement on them. In extreme cases, special paths are laid. Roofs are greened with the help of ground cover plants that do not require careful care and are resistant to seasonal changes.
Intensive simple landscaping is a hybrid version of the previous two types. Plants that do not require a large layer of substrate are selected for planting. At the same time, the special organization of the roof layers allows people to be free on its surface.

Sometimes plants are planted in containers and displayed along with. The advantage of this approach is a reduction in the load on supporting structures, a reduction in the soil layer and lower costs for care and maintenance.
Installation of a green roof, detailed video:
How to make a green roof?
A turf roof requires the organization of certain preliminary work for its arrangement. For example, for intensive roofs it is necessary to install a parapet with a height of at least 120 cm.
The technology for creating a green roof includes the following layers:
- ceiling of the building made of reinforced concrete slab;
- waterproofing from roll materials. Usually it is reinforced at the junctions with parapets, walls and drain holes. For flat roofs, a slope of 3-5% is required;
- thermal insulation is made from materials that are resistant to rotting and deformation. These include foam glass, basalt wool, extruded polystyrene foam;
- Geotextiles are laid on top of the insulation. It allows you to protect the lower layers of insulating materials from soil penetration and penetration by plant roots;
- the last layer is the soil mixture on which flowers, bushes and trees will be planted.

A turf roof also has some disadvantages:
- high cost of installation work;
- complex roof installation that requires experience and knowledge;
- Not every roof can be greened. This depends on the load-bearing and rafter system of the house and the design loads.
Large plants (bushes and trees) can damage the waterproofing layer with their roots. This can be avoided by correctly selecting a waterproofing film, as well as coating it with a special agent that prevents roots from growing deeper. In this case, they continue to grow parallel to the waterproofing film. In addition, the most important condition for obtaining a high-quality turf roof is the fulfillment of all project requirements.
In conclusion, I would like to say that a turf roof has a service life much longer than other types of coverings. This is due to the protection of the roofing pie by soil and plants. That is why the initial high cost of such a solution will pay off in the near future.
Norwegian roofs with a lawn instead of tiles is the talk of all neighboring nations. Ironic Swedes have long been drawing Norwegians with grass on their heads instead of hair. Charming lawn roofs have now become as symbolic of the country as popular with tourists as fjords, trolls and salmon.
Grass roofs appeared in Norway and the Faroe Islands in ancient times. It was convenient and economical: building materials were at hand, such roofs did not require special care, served for a long time, and even helped to camouflage from enemies.
Naturally, those who care To preserve traditions, Norwegians still lay them now - grass roofs can be seen on modern hotels and restaurants, on private houses and public transport stops. In some villages, almost half of the roofs sway in the wind like green waves. They say they improve the microclimate, provide reliable heat and waterproofing, and stabilize the temperature in the house.

Many craftsmen do such roofs yourself. The technology is described in detail on the Internet. Several private companies also offer the service in Norway. Although new tools are used when laying grass roofs, the basis is still the original technology and a lot of manual labor, which is why such roofs are somewhat more expensive than ondulin roofs.
First of all it fits several layers of dry bark. To make it waterproof, it can be soaked in sheep fat or blood. Peat, straw, moss are laid on it...

Many people dream of building a cottage with landscape design on the roof a la the Vikings. They say: “Can you imagine when the roof is Mother Earth, how peacefully you will sleep?”
The fact is that in the Norwegian roof there is a real biocenosis in its harmonious balance. Moreover, the roof simply must be moist; grass (and even bushes and trees) feed on this moisture, along with all the microorganisms of living peaty soil. However, it does not require painstaking care only due to the unique features of the Norwegian climate.

Rising this summer on the famous Prestolen rock, using the roots of trees, like steps, you can unravel the secret of the Norwegian fauna. In order for such a thin layer of soil to bear fruit so abundantly, it requires almost daily watering. The humidity and raininess of the Norwegian climate, as is known, is included in the Guinness Book of Records. Anywhere else on the planet, a grass roof would quickly dry out and be blown away by the wind.

It’s also clear where the rain comes from. The Gulf Stream reaches Norway. The warm vapors, in turn, hit the mountain range, cool and rain (in Bergen, on a generally sunny day, I opened my umbrella five times!). Norway's water cycle is the most intense in the world. This is where they have 80 percent of hydropower and generally a surplus of energy, which they generously share with Europe. And what is especially valuable, unlike oil, it is a renewable, or rather, inexhaustible resource! That's physics.
Therefore, the main characteristic The thing about a Norwegian roof is that, with all its functionality, it is also alive and fertile!
In eastern Norway behind the mountain range, where the climate is drier - and there are an order of magnitude fewer roofs with grass.

Who saw it for the first time Norway has earthen roofs, reminiscent of the famous English lawn. The fact that it needs to be cut, watered and rolled for 500 years is all a fairy tale for naive foreigners. Modern lawns have long been rolled out from rolls reinforced with mesh, planted in squares... After a year, it is no different from 500 years old.

But nowhere does it say about the main thing - about its composition. And the whole secret is in the peaty base of the soil of the British Isles. This is why there is no wind erosion there (like ours), this is why the golf ball rolls like on a billiard table. That is why a horse gallops across it without tearing out the turf with its horseshoes, and that is why only on the grass courts of Wimbledon it is possible to cut the lawn to a height of only 8 millimeters (!) - standard for the legendary Grand Slam tournament.
About the same with grass roofs. Their creation is justified only in the conditions of the Norwegian climate and Norwegian turf. In our case, if a craving for roots has awakened, it is better to cover the roof with wood chips.

For several centuries, roofing in Norway was carried out using natural environmental materials. Green roofs in this country do not surprise anyone and are traditional. Since ancient times, the peoples of Scandinavia have made roofs from peat, turf, birch bark and other natural environmental materials. 

The descendants of the Vikings, the Norwegians, highly appreciated this method of roofing and managed to preserve green roofs on their houses to this day. Almost until the beginning of the 19th century, turf was a universal material used to cover roofs in houses of all classes in Norway. 
Over time, materials such as tiles, slate and other roofing materials appeared on the market, which gradually began to replace the traditional Norwegian ecological, beautiful and cute grass roofs. The “advance of civilization” began in the cities, but eventually reached the countryside.

Green grass roofs in Norway were saved from complete extinction by enthusiasts.
They organized and led a movement aimed at reviving long-standing folk traditions. First, open-air museums, holiday houses in the mountains... and then green roofs made of grass and flowers again became simply popular and fashionable.

Indeed, in addition to the fact that such roofing is simply beautiful and gives aesthetic pleasure, it is quite cheap, durable, stabilizes the temperature in the house, improves the microclimate, providing reliable heat and waterproofing. Therefore, green roofs have become popular again and at the same time have become a worthy alternative to new building materials.